Periodic Inventory System Definition, How It Works

Businesses with high inventory turnover, complex inventory management needs, or a need for real-time inventory levels may prefer the perpetual inventory system. On the other hand, businesses with low inventory turnover, simple inventory management needs, or limited resources may find the periodic inventory system to be more suitable. It is essential to evaluate the benefits and drawbacks of each system and consider factors such as inventory complexity, business size, and resource availability when deciding which system to use.
Time-Consuming Physical Counts
By understanding the benefits, suitable applications, and effective implementation strategies of this system, businesses can make informed decisions about their inventory management needs. Using this valuation technique, you will calculate the average cost of all of your inventory items that were available during the accounting period. This average cost will be applied to your units sold and units remaining in your inventory. Perpetual systems, on the other hand, constantly update inventory levels, resulting in real-time data.
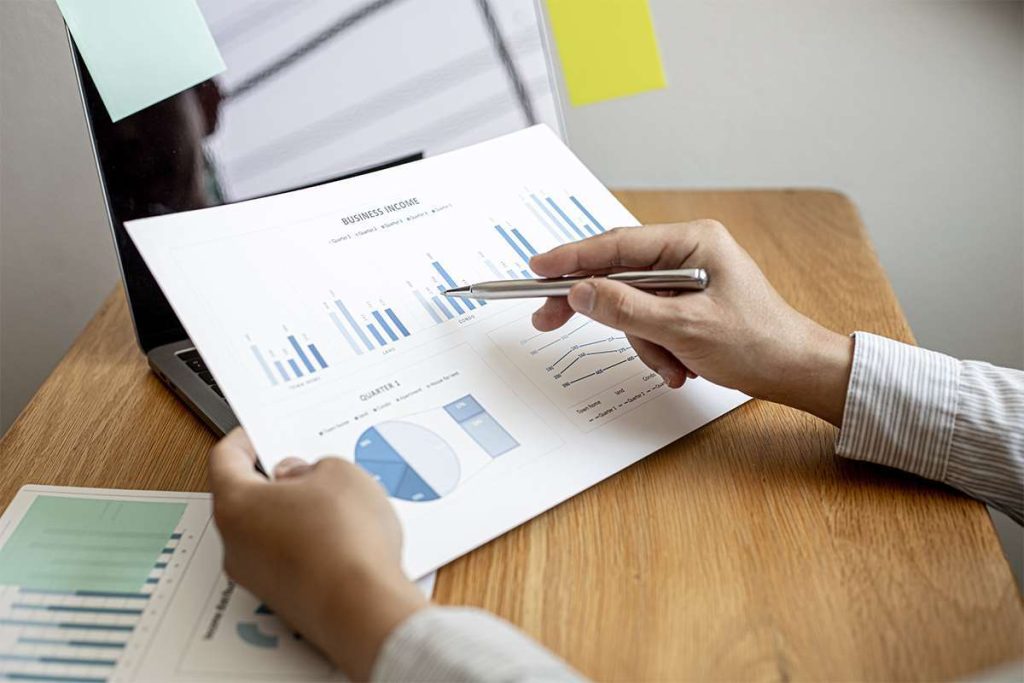

Calculating Periodic Inventory
- The periodic inventory system is also suitable for businesses with stable inventory levels, such as those that sell non-perishable goods or have a predictable demand pattern.
- Latin America and the Middle East & Africa are expected to experience moderate growth, with Turkey and Saudi Arabia showing promise.
- This system involves physically counting the inventory levels at these intervals to determine the quantity of goods on hand.
- In general, we recommend using a periodic inventory management system if you’re trying to track your inventory by hand.
- Factors influencing the landscape include fluctuating oil prices, global production levels, and changing consumer behaviors driven by sustainability concerns.
- A Periodic Inventory System is a method where inventory levels are updated at specific intervals rather than continuously.
While some businesses choose to update their costs, beginning inventory levels, and ending inventory levels frequently, you might not require real-time updates on this information. Periodic inventory systems are one of the simplest accounting processes that still enable a business to monitor its overall inventory. At the end of every period, the purchases account total is added to the beginning inventory. Here are some common questions that business owners have about periodic inventory systems with answers to give you some guidance. Periodic inventory allows a business to track its beginning inventory and ending inventory within an accounting period for their financial statements. Using the periodic inventory method, the total cost of goods sold for the period comes to $350,000.
Journal Entries for Periodic Inventory
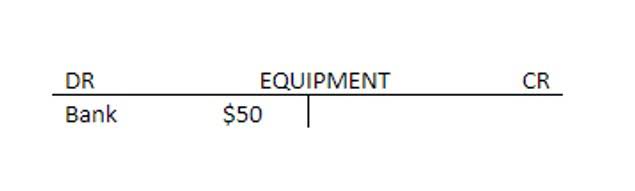
Choosing the right system depends on a company’s size, operational needs, and growth plans. As businesses scale and customer expectations rise, many eventually transition from periodic to perpetual systems for better efficiency and control. What sets the periodic inventory system apart is it only updates inventory ledgers at the end of a period by taking a physical count. Manufacturers, distributors, and retailers can benefit from periodic inventory systems, primarily if they sell in lower volumes and are looking for a simple inventory tracking method. Under the perpetual inventory system, an entity continually updates its inventory records in real time. A purchase return or allowance under perpetual inventory systems updates Merchandise Inventory for any decreased cost.
Effective inventory planning is crucial for ecommerce success, but it’s also one of the biggest challenges businesses face. Last-in, last-out can result in higher COGS and lower ending inventory values during times of inflation, because the more recent and more expensive inventory https://scheltonassoumou.com/2024/06/06/operating-cycle-definition-formula-calculation/ is considered sold first. There are several methods you can use to accomplish this, depending on your financial reporting goals and business objectives. When calculating your cost of goods sold, determine the value of your beginning and ending inventory. Sometimes referred to as COGS, the cost of goods sold is a term that refers to all of the expenses involved in obtaining the products you sell.
That’s why, by comparison, the periodic inventory system is way more tiresome, time-consuming, and prone to error than the perpetual inventory, as everything is done manually. That’s why a periodic inventory system is only mainly used by small businesses with limited inventory and few financial transactions. To determine your business’s profitability, you’ll need to know how much you spent to produce, ship, store, and manage the inventory you’ve sold. Those costs can vary depending on the number of items you order at a time, the amount of inventory sitting in your warehouse, how tightly packed your shipping containers are, and the time spent processing new shipments.
Key Differences Between Periodic and Perpetual Inventory Systems
During periods of inflation, this method results in lower COGS, a higher ending inventory value and higher reported profits. Your accounting period can be any length of time that you desire, and you can always use your remaining stock from your previous accounting period as your beginning inventory. At the end of your accounting period, you’ll update your ending inventory balance and transfer your COGS to an income statement for future tax purposes. Unlike other inventory systems, this method doesn’t implement real-time tracking inventory technology. Therefore, it creates a gap between counting sessions where your business will not have updated stock information. In this FAQ section, we address common questions about perpetual inventory systems, helping you decide if this real-time tracking method is the right fit for your business.
Types of Businesses That Should Use a Periodic Inventory System

Instead, purchases are recorded in a separate purchases account, and inventory balances are only updated after a physical stock count. Since it involves a physical inventory count, it’s not well-suited to vast amounts of inventory that’s rapidly changing. A periodic Inventory System is defined as an inventory valuation method in which inventories are physically counted at the end of a specific period to determine the cost of goods sold. That means ending inventory balance is updated only at the end of the period instead of a perpetual inventory system where inventories are counted periodic inventory frequently. In periodic inventory, the only time records are entirely accurate are at the beginning and end of the period. For the rest of the period, a business relies on estimations of its current inventory levels.
- Periodic inventory can also be more prone to human error as it relies on physical inventory audits rather than a more automated system that’s tracked digitally.
- The arrangement of the elements in the periodic table comes from the electronic configuration of the elements.
- Businesses physically count their inventory at the end of an accounting period such as weekly, monthly, quarterly, or annually to determine stock levels.
- The total inventory value is the cost (or total price) of goods that are able to be sold – minus the total number of goods sold between physical inventories.
- Merchandising businesses that deal with hundreds of transactions a day, such as grocery stores or pharmacies, can’t possibly maintain their inventory through a periodic inventory system.
Differences could occur due to mismanagement, shrinkage, damage, or outdated merchandise. Shrinkage is a term used when inventory or other assets disappear without an identifiable reason, such as theft. For a perpetual inventory system, Foreign Currency Translation the adjusting entry to show this difference follows. This example assumes that the merchandise inventory is overstated in the accounting records and needs to be adjusted downward to reflect the actual value on hand. The periodic inventory system works by setting a specific period, such as a month, during which all inventory transactions are recorded. At the end of the period, the inventory is physically counted, and the results are compared to the recorded transactions.
- Most accounting software use a perpetual inventory system to track and update inventory purchases, sales and the cost of goods in real time.
- The market faces several challenges and risk factors that significantly impact its dynamics.
- Sales Discounts, Sales Returns and Allowances, and Cost of Goods Sold will close with the temporary debit balance accounts to Income Summary.
- The periodic inventory system refers to conducting a physical inventory count of goods/products on a scheduled basis.
- The periodic inventory approach is primarily used by small businesses that deal with very few transactions, or companies that only have a limited number of inventory.
- Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice can significantly impact financial statements and tax liabilities.

Knowing the exact costs earlier in an accounting cycle can help a company stay on budget and control costs. Perpetual and periodic inventory systems are different approaches to stock management. Setup costs are lower, but they require more manual work, resulting in increased labor costs. A periodic inventory system measures the inventory levels periodically through physical counts. The perpetual method continuously updates inventory records after each sale or purchase, monitoring the inventory balance. Small business owners with less inventory benefit more from periodic systems than larger merchants.